
RAJGIR
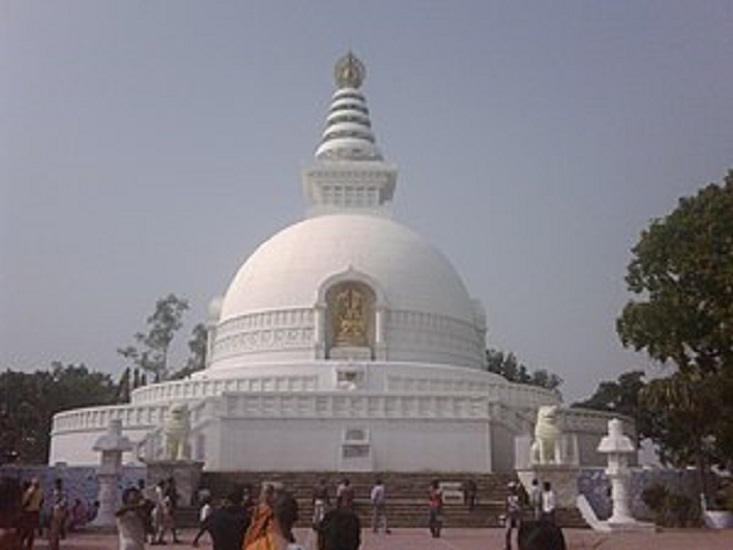

Rajgir (historically known as Rājagṛiha), meaning “the City of Kings”, is an ancient city and a municipal council in Nalanda district of Magadh region in the Indian state of Bihar. The city of Rajgir (ancient Rājagṛha; Pali: Rājagaha) was the first capital of the kingdom of Magadha, a state that would eventually evolve into the Mauryan Empire. The city finds mention in India’s greatest literary epic, the Mahabharata, through its king Jarasandha. Its date of origin is unknown, although ceramics dating to about 1000 BC have been found in the city. The 2,500-year-old Cyclopean Wall is located in the city. This area is also notable in Jainism and Buddhism. It was the birthplace of the 20th Jain Tirthankar Munisuvrata, and is closely associated with the Arihant Mahavira and Gautama Buddha. Both Mahavira and Buddha taught their beliefs in Rajgir during the 6th and 5th century BC, and the Buddha was offered a forest monastery here by the king Bimbisara. As such, the city of Rajgir became one of the Buddha’s most important preaching locations. The ancient Nalanda university was located in the vicinity of Rajgir, and the contemporary Nalanda University named after it was founded in 2010 nearby. It was also through Rajgir that the Mauryan Emperor Ashoka travelled to Bodh Gaya around 250 BC, when placing the diamond throne (Vajrasana) at the great temple where Buddha attained enlightenment.










![Monuments of Mahabodhi [Mahavihara] Temple Complex Bodhgaya](https://baruasamaj.ezdivi.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2023/10/Monuments-Book-Title-150x150.png)


